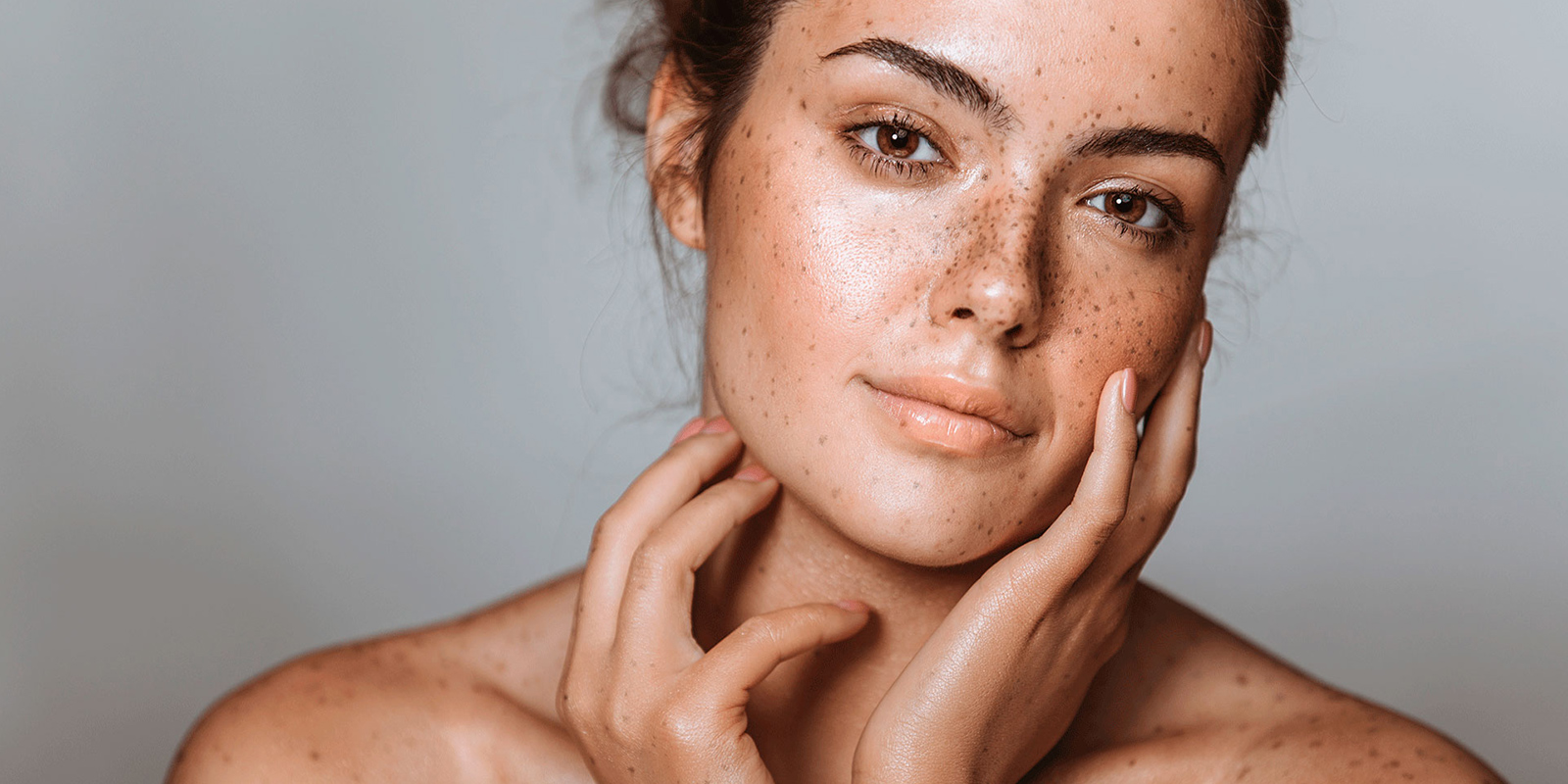
The color of a person’s skin is usually determined by their phototype and how much sun exposure they get; areas frequently exposed to the sun are darker than those that are covered. Melanin is the natural pigment that controls skin color, which the body secretes to protect skin from UV rays, leading to tanning.
Pigmentation problems are linked to poor melanin functioning, which causes either hyperpigmentation (dark spots) or depigmentation (lighter spots) on the skin. The latter is usually related to a condition such as vitiligo or albinism, which requires medical care.
The skin has a natural color, independent of sun exposure: this is its pigmentation.
This color depends on skin cells called melanocytes, which are unique in that they produce pigments known as melanin. This melanin found in the skin offers natural protection against the ultraviolet (UV) rays emitted by the sun.